
Abbreviation For Hazel Eye Color
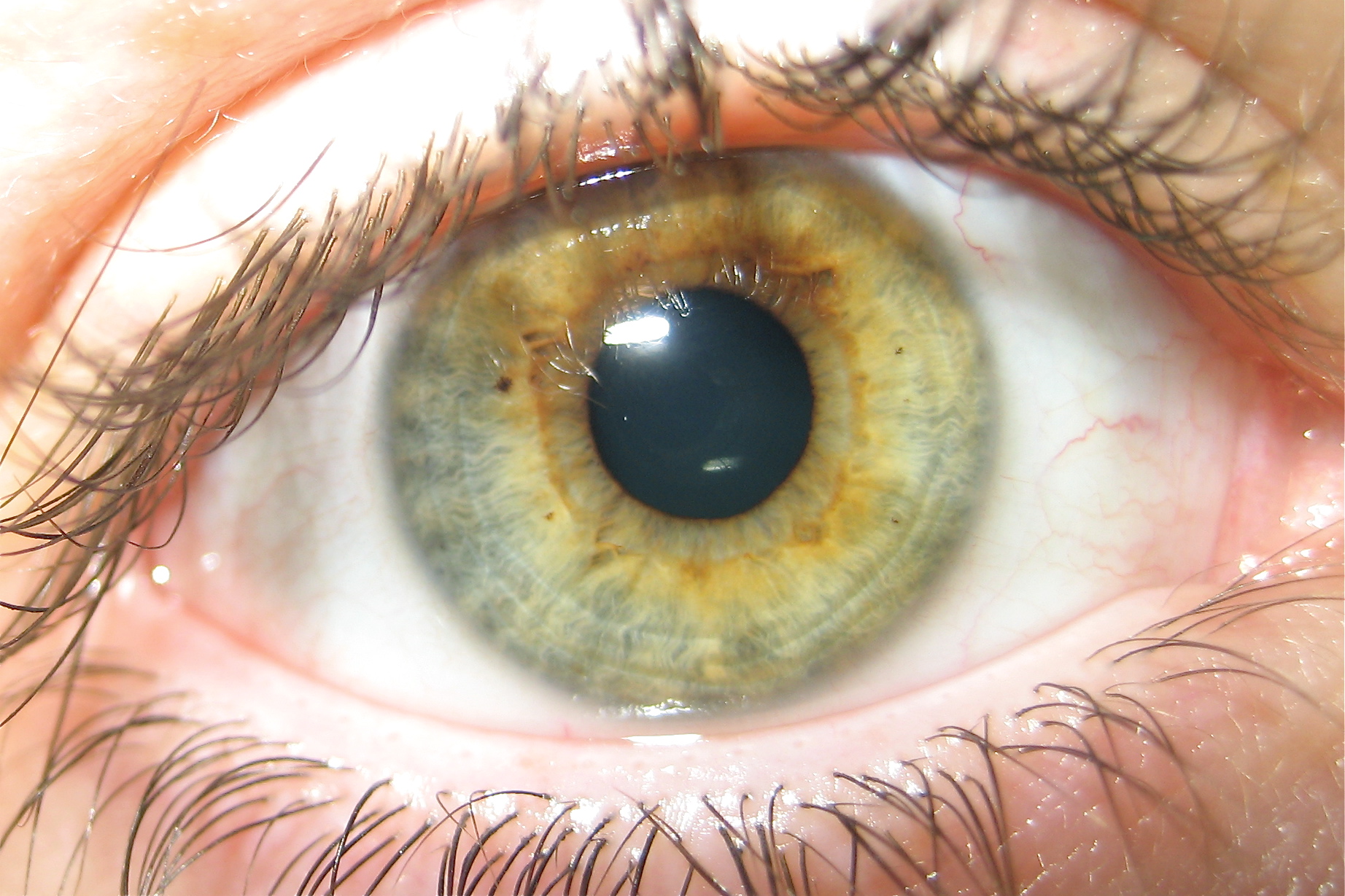
Driver License Endorsements and Restrictions Endorsements. Individuals may apply for an endorsement to be placed on their driver license. Depending on the type of endorsement, an individual may be required to provide additional information, complete a separate application, or pass a knowledge test specific to the type of endorsement the individual is seeking. DRIVER LICENSING ABBREVIATION CODES WITH CHARGE POINTS BDS1 WISCONSIN DEPARTMET OF TRANSPORTATION Footnotes 1. M = mandatory 2. CUL, DS, FDL, GCV, GPV, IB, IE, OAR, OML, OSB, OWD, OWL, OWS, UA, VOO, VOR and pointable non-s.346 violations of FOS, IL, IR and POH were HTO minors prior to 7/27/05. Oct 25, 2019 Abbreviation For Hazel Eyes On Drivers License Eye color Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris. Driver License Renewal Current Ohio License. In an effort to ensure greater security and identity protection for customers, and to comply with federal regulations, the Ohio Bureau of Motor Vehicles introduced a new Ohio driver license and identification (DL-ID) card, effective July 2, 2018.
Abbreviation For Hazel Eyes On Driver's License Requirements
- Eye color
- Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.In humans, the pigmentation of the iris varies from light brown to black, depending on the concentration of melanin in the iris pigment epithelium, the melanin content within the iris stroma, and the cellular density of the stroma. The appearance of blue, green, as well as hazel eyes results from the Rayleigh scattering of light in the stroma, a phenomenon similar to that which accounts for the blueness of the sky. Neither blue nor green pigments are ever present in the human iris or ocular fluid. Eye color is thus an instance of structural color and varies depending on the lighting conditions, especially for lighter-colored eyes.The brightly colored eyes of many bird species result from the presence of other pigments, such as pteridines, purines, and carotenoids. Humans and other animals have many phenotypic variations in eye color. The genetics of eye color are complicated, and color is determined by multiple genes. So far, as many as 15 genes have been associated with eye color inheritance. Some of the eye-color genes include OCA2 and HERC2. The once-held view that blue eye color is a simple recessive trait has been shown to be incorrect. The genetics of eye color are so complex that almost any parent-child combination of eye colors can occur. However, OCA2 gene polymorphism, close to proximal 5′ regulatory region, explains most human eye-color variation.